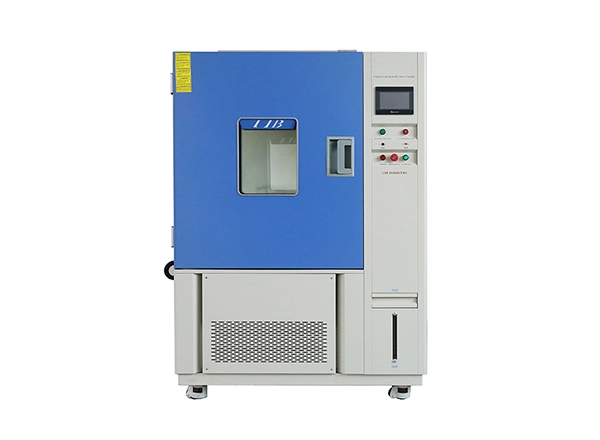
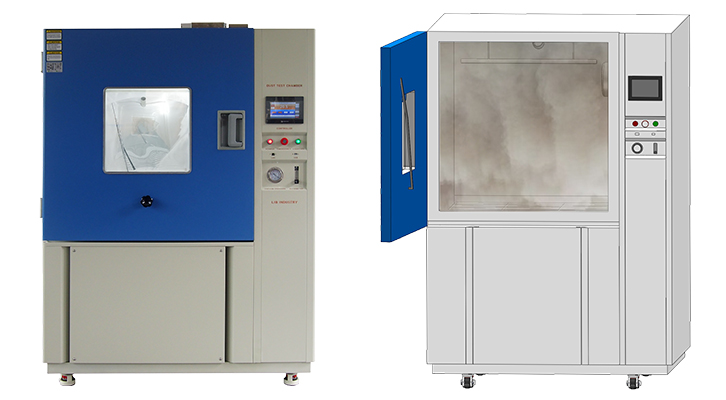
Batteries must remain safe and reliable even under sudden temperature swings—from freezing cold to scorching heat. To ensure this, manufacturers turn to the thermal shock tester, which replicates extreme hot-to-cold transitions in the lab. A two zone thermal shock tester is especially effective for battery cells, uncovering weaknesses and validating durability.

This article explains how the technology works and how LIB’s thermal shock chamber provides precise and customizable solutions.
A thermal shock tester is a laboratory device that subjects specimens to sudden temperature changes, simulating real-world stresses that occur when materials or components experience rapid transitions between hot and cold environments.
Two-zone design: In this configuration, the chamber consists of a hot zone and a cold zone. The specimen is automatically transferred between the two environments.
Temperature extremes: The cold zone can reach −75 °C, while the hot zone can reach +220 °C.
Cycle accuracy: Precise timing and control ensure repeatable results, which is critical for safety-critical products like batteries.
LIB offers a range of models suitable for small battery cells up to large EV modules. Below is a typical configuration for a two zone thermal shock tester:
Parameter | Specification |
Temperature Range (Cold Zone) | −70 °C to Ambient |
Temperature Range (Hot Zone) | Ambient to +200 °C |
Transfer Time | ≤ 10 seconds |
Recovery Time | ≤ 5 minutes |
Basket Capacity | 20kg ~ 60kg (customizable) |
Test Chamber Volume | 22L – 505L (custom sizes available) |
Control System | PLC + Touchscreen Interface |
Safety Features | Over-temp protection, door interlock, emergency stop |
 | |
LIB also provides custom designs, allowing clients to adjust chamber size, transfer speed, or add extra safety features depending on battery type and regulatory needs.
When testing lithium-ion or other advanced batteries, the thermal shock tester follows a structured process:
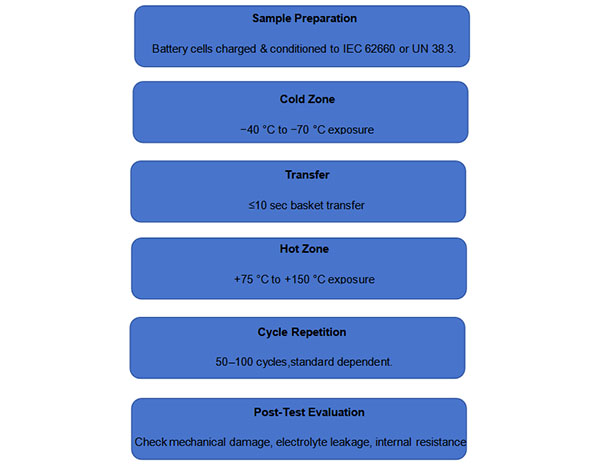
Sample Preparation
Battery cells are preconditioned and fully charged according to IEC 62660 or UN 38.3 requirements.
Test Cycle
The sample is placed in the transfer basket.
It is exposed alternately to the cold zone (−40 °C to −70 °C) and hot zone (+75 °C to +150 °C).
Transfer between zones takes less than 10 seconds to replicate sudden environmental change.
Number of Cycles
Typically 50–100 cycles, depending on the standard or customer-specific requirements.
Monitoring
Temperature sensors, voltage, and current are continuously recorded.
The tester monitors any abnormal swelling, venting, or leakage.
Post-Test Evaluation
Cells are inspected for mechanical damage, electrolyte leakage, internal resistance, and capacity retention.

LIB’s thermal shock chambers comply with international testing standards, making them ideal for regulated industries:
UN 38.3 – Safety testing for lithium batteries during transportation.
IEC 62660-2 – Secondary lithium-ion cells for the propulsion of electric vehicles.
SAE J2464 – Electric vehicle battery abuse testing.
MIL-STD-883 – Thermal shock testing for electronic components.
By following these recognized standards, manufacturers can ensure global compliance while enhancing safety and performance validation.
While battery testing is one of the most critical uses, a thermal shock tester is versatile across industries:
Electronics: Solder joints, PCB boards, and connectors.
Automotive: ECUs, sensors, and control modules.
Aerospace and defense: Materials and components exposed to extreme climates.
Medical devices: Ensuring stable performance under thermal stress.
A two zone thermal shock tester is indispensable for ensuring the safety, durability, and performance of battery cells and other sensitive components. By replicating rapid hot-to-cold transitions, it exposes hidden weaknesses and ensures compliance with global standards.
LIB’s thermal shock chamber solutions combine precision engineering, fast transfer systems, and flexible customization. Whether for small coin cells or large EV modules, LIB delivers industry-leading equipment to help manufacturers achieve the highest levels of safety and reliability.
 English
English русский
русский français
français العربية
العربية Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español 한국어
한국어 italiano
italiano tiếng việt
tiếng việt ไทย
ไทย Indonesia
Indonesia