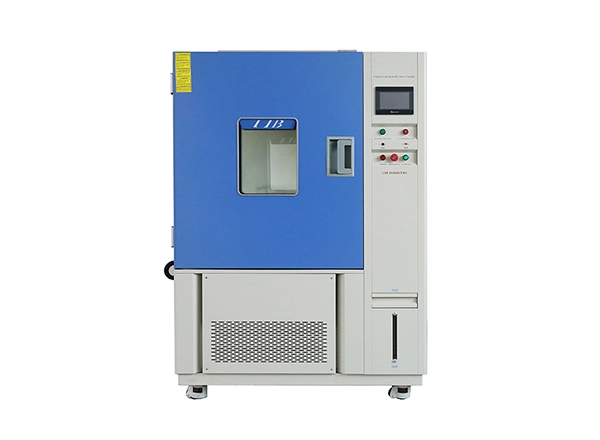

From electronics and automotive systems to aerospace components and advanced materials research, thermal cycling provides a controlled and repeatable method to simulate real‑world thermal stress.
The thermal cycling chambers are essential tools for evaluating the durability, reliability, and structural integrity of materials and components exposed to fluctuating thermal environments. This document presents best practices for operating and maintaining thermal cycling chambers, with special insight into the advanced features of LIB Industry’s thermal cycling solutions.
A thermal cycling chamber operates by rapidly alternating the internal environment between low and high temperatures according to a programmed schedule. Three major subsystems govern its performance:

Advanced PID control algorithms maintain ultra‑stable temperature output.
Real‑time feedback loops ensure minimal deviation, guaranteeing test repeatability.
Multi‑segment programmable profiles support complex temperature curves.
High‑power electric heaters raise the temperature quickly to meet ramp‑rate requirements.
A refrigeration compressor lowers the temperature efficiently, defining the thermal test chamber’s minimum temperature down to -70℃ and cooling rate.
Air circulation fans ensure uniform airflow and temperature distribution across all specimen positions.
Integrated alarms for over‑temperature, compressor overload, door open, and system faults.
Real‑time display for temperature, program progress, and system status.
Together, these systems create a controlled thermal environment that enables accurate, repeatable, and fast cycling—perfect for high‑demand R&D and production applications.
Operating a thermal cycling equipment correctly ensures consistent performance, reduces downtime, and protects test accuracy. Below are refined, industry‑proven practices.
Before starting a thermal cycling test, confirm the following:
Power supply is stable and matches equipment specifications.
Chamber interior is clean and unobstructed.
Door gasket is properly sealed.
Water level (if applicable) meets operating requirements.
Refrigeration system shows no abnormal noise or vibration.
Arrange test samples with sufficient spacing.
Avoid blocking sensor areas or air outlets.
Use LIB Industry‑approved sample fixtures for best thermal uniformity.
Well‑planned loading improves temperature consistency and reduces cycle times.
Set the program according to test standards such as IPC‑9701, ISO 16750‑4, or MIL‑STD‑810H Method 503. Key parameters include:
Temperature Range: e.g., –40°C to +150°C
Ramp Rate: 3–15°C/min, depending on chamber performance
High Temp Dwell Time: 10–60 minutes
Low Temp Dwell Time: 20–60 minutes
Cycle Count: 50–500 depending on reliability objectives
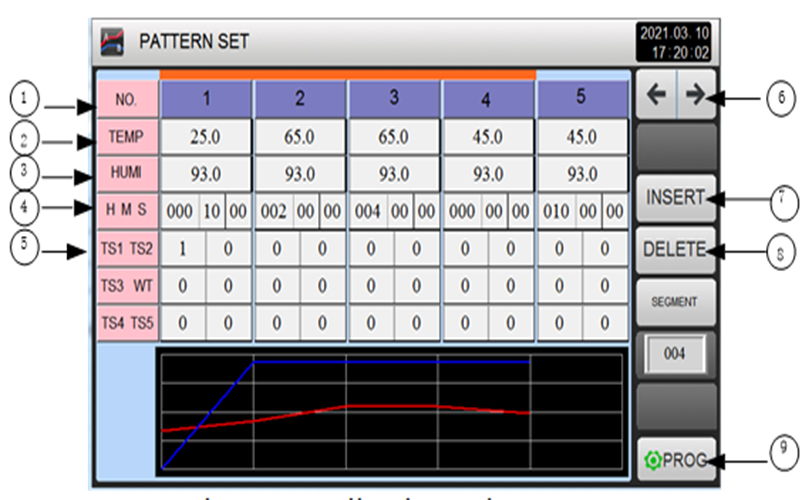
Example Application:
An automotive ECU module undergoing validation:
–40°C → +125°C
10°C/min ramp
30‑minute dwell at each extreme
300 cycles total
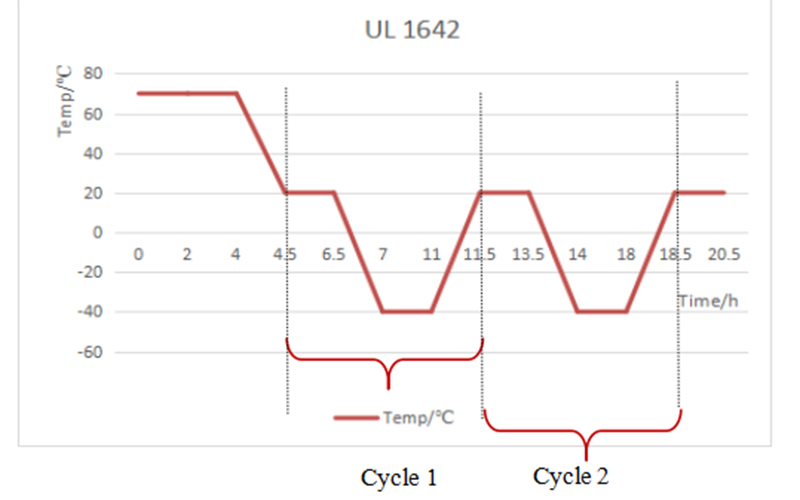
Verify temperature deviation remains within ±0.5°C (temperature) or ±2% RH (if humidity is enabled).
Observe system load, compressor cycling frequency, and airflow stability.
Immediately pause the program if unusual noise, temperature drift, or alarm occurs.
Consistent monitoring ensures test integrity and prevents unnecessary downtime.
Routine maintenance is not optional—it directly determines the accuracy, safety, and longevity of your temperature cycling chamber .
Wipe interior surfaces to prevent dust accumulation.
Ensure door gasket maintains airtight sealing.
Check for abnormal sensor readings or temperature drift.

Clean condenser and evaporator surfaces using compressed air or a soft brush.
Inspect fan blades for wear, looseness, or vibration.
Lubricate hinges and mechanical components as recommended.
Calibrate temperature sensors using a certified reference thermometer.
Inspect refrigerant pressure and cooling performance.
Replace aging door gaskets and worn internal components.
Verify controller firmware and system functions.
Test using standard specimens (e.g., metal blocks with known thermal properties) to confirm:
Temperature uniformity
Stabilization time
Rise/fall rates
Repeatability across multiple cycles
Many equipment failures and data inaccuracies trace back to improper operation.
Avoid:
Overloading the chamber, causing poor airflow and unstable temperature distribution.
Blocking air channels with improper sample placement.
Setting ramp rates beyond equipment capability, stressing the compressor.
Allowing the chamber to operate with a damaged gasket, causing leakage and energy waste.
Neglecting refrigeration system maintenance, leading to premature compressor failure.
LIB Industry provides advanced, reliable, and customizable thermal cycling systems designed for professional laboratories and industrial production environments.LIB Industry is a global supplier with over 16 years of experience trusted by electronics manufacturers, automotive suppliers, aerospace institutions, universities, and government laboratories.
Wide Temperature Range: –70°C to +150°C customizable.
High Ramp Rates: 3–15°C/min for rapid temperature transitions.
Touchscreen Controller: User-friendly 7–10 inch interface with multi‑segment programmable profiles.
Precision Control: ±0.5°C accuracy and excellent temperature uniformity.
Non‑standard dimensions
High‑ramp‑rate models
Special airflow structures
Multi‑cable ports
CE-compliant safety architecture
Industrial‑grade compressors
Reinforced insulation and long‑life components
Technical support for installation, calibration, and training
Q1: What is the IEC standard for thermal cycling?
IEC 60068‑2‑14 is the primary standard describing temperature cycling, rapid changes of temperature, and thermal shock methods used for reliability testing in electronic and electromechanical products.
Q2: What is the thermal cycling process?
Thermal cycling consists of repeatedly transitioning a product between low and high temperatures with controlled ramp rates and dwell periods. This process accelerates fatigue, identifies solder joint weaknesses, and validates long‑term durability.
Q3: How does a thermal chamber work?
A thermal chamber uses heaters, refrigeration compressors, airflow circulation, and a precision controller to create and maintain rapid temperature transitions according to programmed profiles.
Q4: What is the standard for temperature cycling tests?
Common standards include IEC 60068‑2‑14, MIL‑STD‑810H Method 503, IPC‑9701, and ISO 16750‑4, each specifying test conditions, ramp rates, cycle counts, and performance evaluation criteria.
LIB Industry not only supplies advanced rapid rate thermal cycling chamber but ensures fast, dependable service worldwide.

7~15 Days Quick Production & Delivery: Optimized manufacturing and stock models shorten lead times.
1~3 Hours Responsive Technical Support: Remote guidance, diagnostics, and troubleshooting available anytime.
3-Year Global After‑Sales Service: Installation, calibration, and operator training for smooth startup.
Long‑Term Partnership: Spare parts, maintenance plans, and lifetime support ensure sustained reliability.
Choose LIB Industry inquiry@libtestchamber.com for rapid response, smooth communication, and long‑lasting confidence in every thermal cycling project.
 English
English русский
русский français
français العربية
العربية Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español 한국어
한국어 italiano
italiano tiếng việt
tiếng việt ไทย
ไทย Indonesia
Indonesia_Compliance_Guide_How_LIB_Industry_Stability_Chambers_Accelerate_Pharmaceutical_Registration2_20251230154049.webp)


