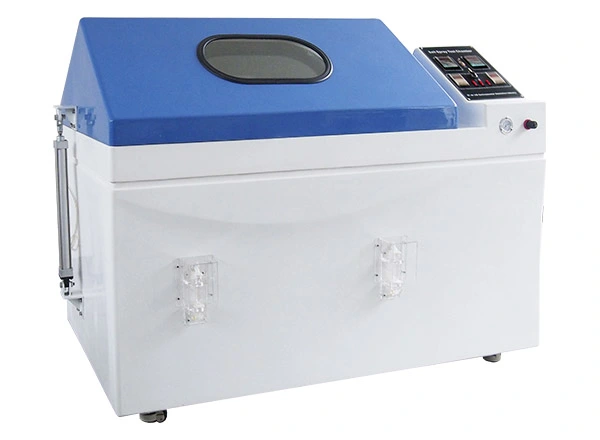

Corrosion resistance is a fundamental quality requirement in the automotive industry. From structural fasteners to coated exterior panels and electronic connectors, automotive components are continuously exposed to aggressive environments such as road salt, marine humidity, rainwater, and industrial pollutants. Over time, these factors can lead to material degradation, coating failure, electrical malfunction, and even safety risks.
To prevent such failures before products reach the market, automotive manufacturers and suppliers rely on salt spray chambers to conduct accelerated corrosion testing. By reproducing corrosive salt-laden environments under controlled conditions, salt spray chambers help verify whether automotive parts can meet durability expectations and pass corrosion standards required by OEMs and international regulations.
Many automotive manufacturers have found that using LIB Industry salt spray chambers significantly improves their production quality control. Teams report that the chambers deliver consistent, repeatable results and simplify compliance with international corrosion standards. Engineers especially value the precise control over temperature, humidity, and spray conditions, which allows them to efficiently test different types of coatings and components without delays.
In real-world driving conditions, corrosion is unavoidable. Vehicles operate year-round, often in regions where de-icing salts are used extensively, or in coastal areas with high salt content in the air. These environments accelerate corrosion processes and can quickly expose weaknesses in materials or surface treatments.
If corrosion resistance is insufficient, the consequences are costly:
Reduced mechanical strength and functional reliability
Premature appearance degradation
Increased warranty claims and recalls
Failure to meet OEM validation requirements
For this reason, corrosion testing is not optional in automotive development. Salt spray corrosion testing has become a baseline requirement across design validation, supplier qualification, and routine quality control.
Salt spray testing is applied to a wide range of automotive components, each with different exposure risks and performance expectations. Understanding these requirements helps manufacturers select the right testing strategy—and the right salt spray chamber.
Automotive Part | Corrosion Risk | Typical Test Objective |
Fasteners & bolts | Red rust formation | Structural reliability |
Brake components | Functional corrosion | Safety performance |
Coated metal parts | Coating blistering or peeling | Surface durability |
Electrical connectors | Oxidation of contacts | Signal stability |
These components vary greatly in size, geometry, and quantity, which places high demands on the salt spray chamber’s internal space, spray uniformity, and environmental stability.
A salt spray corrosion test chamber accelerates corrosion by recreating harsh environmental conditions in a controlled and repeatable way. Instead of waiting months or years for natural corrosion to occur, automotive engineers can evaluate corrosion performance within a much shorter test cycle.

LIB industry salt spray chambers simulate a salt fog marine climate using a standard 5% sodium chloride solution, which reflects typical road salt and coastal exposure. Inside the chamber, a high-humidity environment of 95% to 98% RH is maintained to promote electrochemical corrosion reactions, while the temperature is precisely controlled within a range of ambient to +60 °C.
These controlled parameters ensure that corrosion occurs consistently across test samples, allowing reliable comparison between different materials, coatings, or surface treatments.
Automotive corrosion testing must comply with internationally recognized standards to ensure consistency and acceptance throughout global supply chains. Salt spray chambers are therefore designed not only to generate corrosion, but to do so in strict accordance with test specifications.
Commonly used standards include:
ASTM B117 – Neutral salt spray testing
ISO 9227 – NSS, AASS, and CASS corrosion tests
ASTM G85 – Modified and cyclic salt spray testing
SAE J2334 – Cyclic corrosion testing for automotive applications
A salt spray chamber must support these standards through precise control of temperature, humidity, salt concentration, and spray deposition rate. Without this level of control, test results may lack repeatability and fail to meet audit or certification requirements.
LIB industry Salt Spray Cabinets are specifically designed to reproduce salt fog environments commonly encountered by automotive parts. Using a standard 5% salt solution, the chambers are suitable for evaluating corrosion performance of metal surfaces, platings, and coatings under accelerated conditions.
Both neutral and acidified salt spray environments can be generated, allowing manufacturers to test everything from basic metal fasteners to high-performance decorative coatings.
 |  | |||
Model | S-150 | S-250 | S-750 | S-010 |
Interior Volume (L) | 110 | 320 | 410 | 780 |
Temperature Range | Ambient ~ +60 ℃ | |||
Humidity Range | 95% ~ 98% RH | |||
Salt Fog Deposition | 1~2ml / 80cm2 · h | |||
Spray Type | Continuous / Periodic | |||
Salt Fog Collected | Fog collector and fog measure cylinder | |||
Air Preheating | Saturated air barrel | |||
Spraying System | Atomizer tower and Spray nozzles | |||
Controller | PID controller | |||
Material | Glass fiber reinforced plastics | |||
Standard Configuration | 6 round bars and 5 V-shaped grooves | |||
Reliable corrosion testing depends on environmental stability. LIB industry salt spray chambers provide precise control over key parameters that directly influence test results:
Temperature range: Ambient ~ +60 ℃
Temperature fluctuation: ±0.5 ℃
Temperature deviation: ±2.0 ℃
Humidity range: 95% ~ 98% RH
Salt fog deposition: 1–2 ml / 80 cm²·h
These controlled conditions ensure excellent test repeatability, which is critical when comparing results across batches, suppliers, or development stages.
Different automotive components require different corrosion test methods. LIB industry salt spray chambers support the main test types used in automotive validation:
Test Type | Salt Solution | Automotive Application |
NSS (Neutral Salt Spray) | Neutral 5% NaCl | General metal and coating evaluation |
AASS / CASS | Acidified salt solution | High-performance and decorative coatings |
This flexibility allows a single chamber to support multiple test standards and automotive applications.
Uniform salt fog distribution is essential to avoid localized over-corrosion or under-exposure. LIB industry chambers use optimized spray towers, atomizer systems, and corrosion-resistant quartz nozzles to ensure even salt fog dispersion throughout the test space.
An integrated saturated air barrel preheats compressed air before atomization, further stabilizing spray conditions and improving consistency across long-duration tests.
Automotive laboratories often run corrosion tests continuously. To support long-term operation, LIB industry salt spray chambers are constructed from integrally formed glass fiber reinforced plastics (GRP). This material offers high mechanical strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and long service life, making it well suited for high-frequency automotive testing environments.
|
|
| Corrosion-Resisitant Workroom | Modular grooves are used for holding samples |
salt spray tower |
cylinder |
spray collector |
Modern automotive testing laboratories demand efficiency, traceability, and ease of use. LIB industry salt spray chambers are equipped with touchscreen PID controllers that allow users to program test cycles, adjust parameters, and monitor test status in real time.
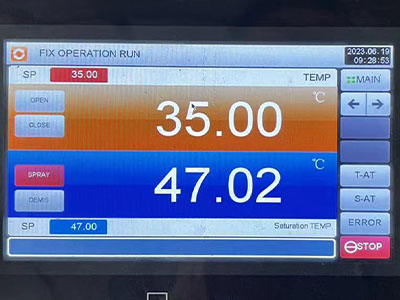
Key operational features include:
Continuous or periodic spray modes
Multi-language user interface
USB data export and PC remote control
Built-in safety protections for temperature, water level, and electrical systems
These features reduce operator workload, minimize human error, and support reliable documentation for quality audits.
Automotive corrosion testing involves a wide variety of sample sizes and test volumes. LIB industry offers multiple salt spray chamber models to support flexible selection.
Model | Internal Volume (L) | Typical Use |
S-150 | 110 | Small components and fasteners |
S-250 | 320 | Routine quality control |
S-750 | 410 | Batch testing of coated parts |
S-010 / S-016 / S-020 | Up to 780 | Large panels and assemblies |
In addition to standard models, customized salt spray chambers are available. LIB industry can provide tailored chamber dimensions, specialized sample holders, and configurations designed for automotive electronics, new energy vehicle components, or other specific applications.
While salt spray chambers focus on corrosion caused by salt and humidity, automotive components are also exposed to sunlight and weathering. For a more comprehensive durability assessment, corrosion testing is often combined with UV or Xenon test chambers, particularly for coatings, plastics, and interior or exterior trim materials.
By combining salt spray testing with UV or Xenon exposure, manufacturers can better simulate real-world aging conditions and improve long-term product reliability. LIB industry provides UV and Xenon test chambers to support these complementary testing requirements.
Salt spray chambers play a vital role in helping automotive parts pass corrosion tests and meet durability expectations. From fasteners and brake components to coated panels and electrical connectors, reliable corrosion testing reduces risk, improves quality, and supports compliance with international standards.
With precise environmental control, flexible test modes, durable construction, and customizable configurations, LIB industry salt spray chambers offer dependable solutions for automotive corrosion testing.
If you are looking for a reliable salt spray chamber to support your automotive testing requirements, contact LIB industry to discuss your application and customized solutions.a 3-year warranty, lifelong technical support, and responsive English-speaking service—ensuring reliable, worry-free operation throughout the equipment lifecycle.
 English
English русский
русский français
français العربية
العربية Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español 한국어
한국어 italiano
italiano tiếng việt
tiếng việt ไทย
ไทย Indonesia
Indonesia







