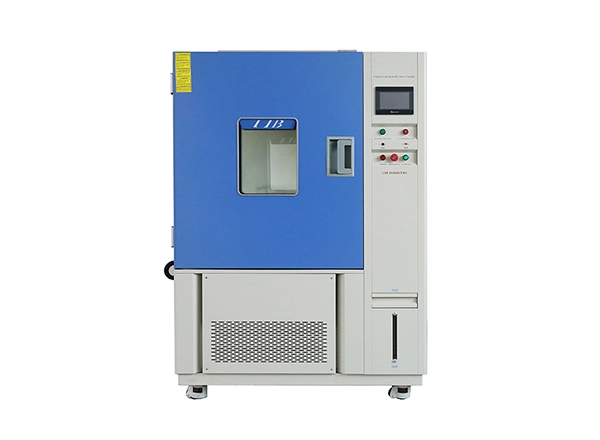
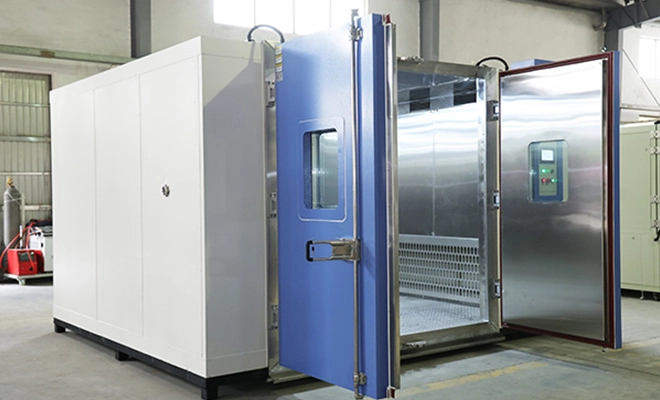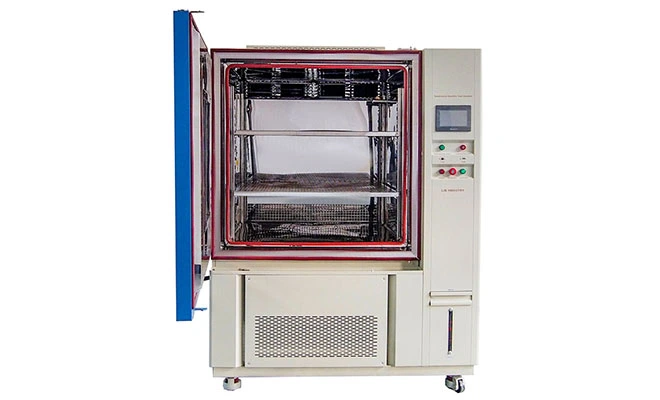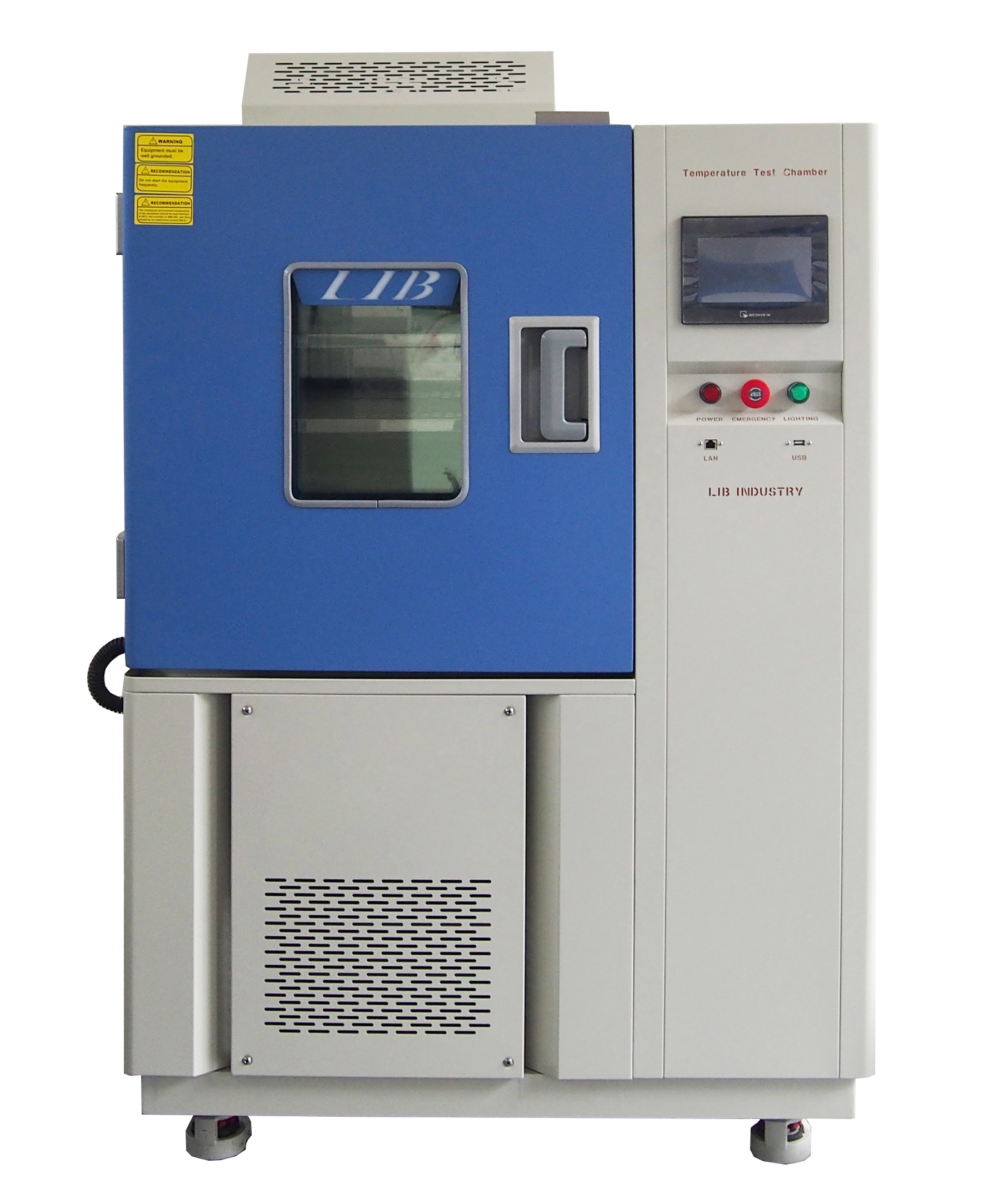

Drug stability is one of the most critical challenges in the pharmaceutical industry. Pharmaceutical products range from chemically synthesized small-molecule drugs to complex biologics derived from living organisms or biotechnology processes. Due to their different physical and chemical characteristics, these drugs respond very differently to temperature variations.

In pharmaceutical testing and storage, temperature is not a background condition—it is a key stability factor that directly affects drug safety, efficacy, and shelf life.
Biologic drugs are particularly sensitive to temperature due to their protein-based structures:
Slight temperature increases may cause protein denaturation
Structural deformation can result in loss of pharmacological activity
Once denatured, biological activity is often irreversible
Even minor temperature deviations during testing or storage can compromise product efficacy.
For certain liquid preparations, excessively low temperatures can also pose risks:
Solutes may crystallize under low-temperature conditions
Concentration ratios can change, affecting dosage accuracy
Crystallization may block injection needles and increase patient risk
These issues highlight the necessity of controlled and repeatable temperature environments during stability evaluation.
Drugs designed for long-term storage are continuously exposed to environmental temperature changes during warehousing, transportation, and daily handling. Over time, even small and repeated temperature cycles can act as a cumulative degradation factor, leading to:
Chemical degradation
Increased impurity levels
Reduced therapeutic effectiveness
This makes temperature control a long-term quality safeguard, not just a short-term testing requirement.
During early drug development, uncertainty is unavoidable. Temperature chambers are essential tools for formulation screening and stability comparison at this stage.
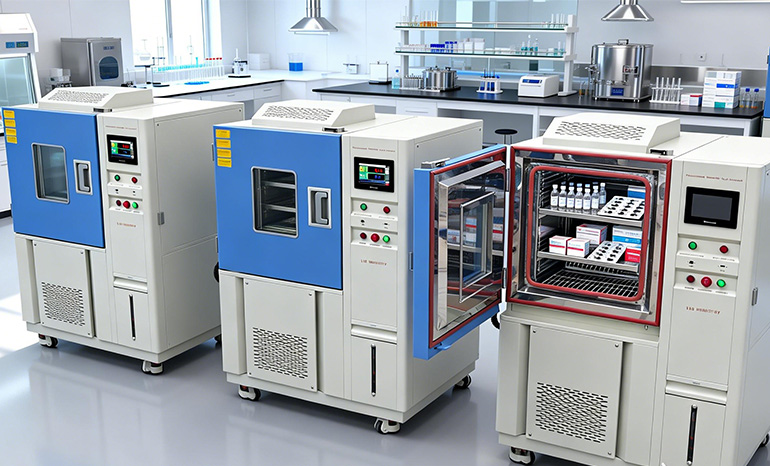

Typical applications in R&D include:
Evaluating formulation behavior under high and low temperature stress
Simulating daily or seasonal temperature cycles
Comparing structural stability across multiple compound candidates
By observing physical and chemical changes under controlled temperature conditions, researchers can identify formulations with stable structures and reliable performance, providing a strong foundation for further development.
High low temperature test chamber remain indispensable throughout pharmaceutical manufacturing and quality assurance processes.
Incoming raw materials are routinely evaluated under controlled temperature conditions. For example, capsule gelatin quality may vary due to temperature differences during upstream processing. Temperature chambers help verify whether gelatin maintains consistent gelling performance under both standard and extreme temperature conditions before being approved for production use.
In antibiotic production, fermentation temperature directly influences active ingredient consistency. Even minor temperature deviations can lead to batch variability. By simulating different fermentation temperature scenarios in a constant temperature chamber, manufacturers can:
Analyze temperature impact on active ingredient yield
Optimize process parameters
Ensure batch-to-batch consistency
This process validation is essential for maintaining stable drug quality at scale.
Temperature chambers continue to play a vital role after drugs enter the market. According to regulatory requirements, pharmaceutical companies routinely conduct post-marketing stability studies using market samples.
These studies typically involve:
Long-term exposure under controlled storage conditions
Periodic testing for impurity growth and potency loss
Data collection for regulatory inspection and audit
If abnormalities are detected, manufacturers can promptly adjust storage recommendations or initiate corrective actions, minimizing risks to patient safety.
Pharmaceutical stability evaluation primarily relies on two complementary testing approaches.
Accelerated stability testing simulates long-term drug aging within a shorter timeframe by applying elevated temperature and controlled humidity conditions.
Typical objectives include:
Predicting potential degradation pathways
Estimating shelf life during early development
Supporting formulation screening decisions
This method significantly improves R&D efficiency while providing valuable predictive data.
Long-term stability testing records real-time changes under conditions close to actual storage environments. These data are essential for:
Determining accurate expiration dates
Optimizing storage and transportation conditions
Supporting regulatory submissions and approvals
Pharmaceutical stability studies are conducted within well-established regulatory frameworks to ensure data reliability and global acceptance. Commonly referenced guidelines include:
ICH Q1A(R2) – Stability Testing of New Drug Substances and Products
ICH Q1B – Photostability Testing of New Drug Substances and Products
GMP requirements for environmental control and data traceability
Temperature chambers used in pharmaceutical testing must support stable conditions, repeatability, and complete data records to meet these regulatory expectations.
For pharmaceutical stability testing, temperature chambers generally provide the following performance characteristics:
Temperature range: –20 °C to +60 °C (customizable)
Temperature fluctuation: ±0.5 °C
Temperature uniformity: ±2 °C
Test modes: accelerated stability and long-term stability
Data logging: continuous recording for audit and compliance
These parameters ensure consistent exposure conditions and reliable test results.
LIB industry temperature chambers deliver stable, repeatable temperature environments for pharmaceutical stability testing.
Temperature fluctuation: ±0.5 °C
Temperature uniformity: ±2 °C
Supports: accelerated and long-term stability studies
Data logging: continuous temperature and humidity records
Model | T-100 | T-225 | T-500 | T-1000 |
Interior Volume | 100L | 225L | 500L | 1000L |
Heat load | 1000W | |||
Temperature Range | A : -20℃ ~ +150 ℃ B : -40℃ ~ +150 ℃ C: -70℃ ~ +150 ℃ | |||
Temperature Fluctuation | ± 0.5 ℃ | |||
Temperature Deviation | ± 2.0 ℃ | |||
Cooling Rate | 1 ℃ / min | |||
Heating Rate | 3 ℃ / min | |||
Cooling system | Environmentally friendly refrigerant,French TECUMSEH compressor,compliant with the GWP standards requirements | |||
Controller | Programmable color LCD touch screen controller, Ethernet connection | |||
 | ||||
These capabilities help pharmaceutical manufacturers generate reliable stability data, reduce test deviation, and meet regulatory inspection requirements with confidence.
LIB industry temperature chambers support pharmaceutical R&D, manufacturing, and post-marketing stability programs by combining precise temperature control, compliance-oriented design, and traceable data records—helping manufacturers protect product quality and patient safety throughout the entire product lifecycle.
Contact LIB industry inquiry@libtestchamber.com to obtain a compliant temperature chamber solution within 1~3 hours for pharmaceutical stability testing across R&D, production, and stability programs.
 English
English русский
русский français
français العربية
العربية Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español 한국어
한국어 italiano
italiano tiếng việt
tiếng việt ไทย
ไทย Indonesia
Indonesia


