
It is essential that products operate stably and reliably in a variety of complex temperature environments. Thermal cycling test and thermal shock test are two commonly used temperature test methods. Although both are related to temperature change, they possess unique characteristics and application scenarios, playing a key role in accurately evaluating product quality and performance.
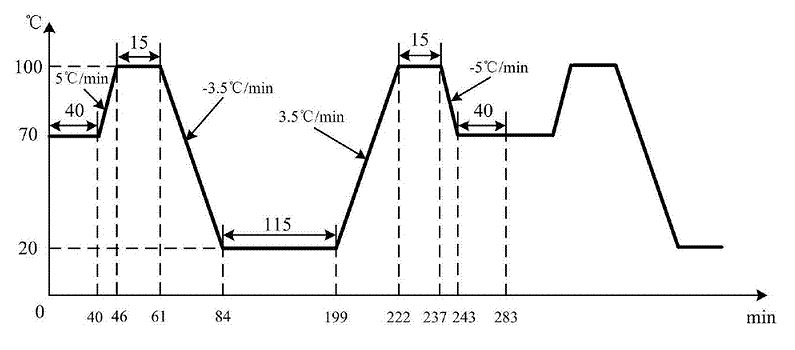
The thermal cycling test evaluates how products perform under continuous temperature variations over a long period. This test simulates repeated heating and cooling cycles to reveal potential material fatigue, microcracks, solder joint failures, or thermal expansion mismatches.
It is widely used in the electronics, automotive, aerospace, and materials industries to ensure reliability and long-term stability.
Test Conditions and Characteristics
Temperature range: from low winter temperatures to high summer conditions.
Heating/cooling rate: typically 5–20°C/min.
Test duration: hours to several days per cycle.
Goal: simulate long-term environmental stress and cumulative thermal effects.
During the thermal cycle, temperature changes are gradual, and stress develops progressively. The test exposes defects such as uneven material expansion, bonding weakness, or coating detachment, improving product durability and design quality.
LIB Industry Thermal Cycling Test Chamber provides precise control for repeated temperature variations, supporting both standard and custom temperature cycles. Using cascade mechanical refrigeration and high-power heating systems, it ensures consistent performance and reliability.
Specifications of Thermal Cycling Chamber
Model | TR5-100 | TR5-225 | TR5-500 | TR5-800 | TR5-1000 |
Interior Volume | 100L | 225L | 500L | 800L | 1000L |
Temperature Range | A: -20~+150°C / B: -40~+150°C / C: -70~+150°C | ||||
Temperature Fluctuation | ±0.5°C | ||||
Temperature Deviation | ±2.0°C | ||||
Cooling & Heating Rate | 5 / 10 / 15 / 20°C per minute (customizable) | ||||
Heat Load | 1000W | ||||
| |||||
Key Features
Programmable multi-step temperature cycles.
Uniform airflow design ensuring temperature consistency.
User-friendly touch-screen control system.
Optional humidity control integration.
|
|
Programmable Controller | Uniform airflow in Workroom |
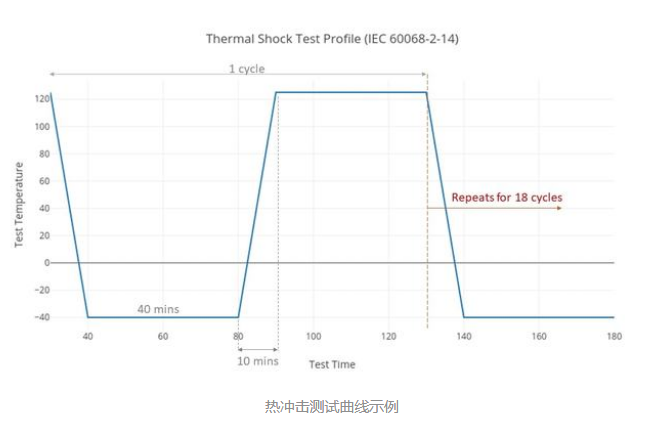
Unlike the gentle transition of thermal cycling, the thermal shock test exposes a product to instant, extreme temperature changes, evaluating its resistance to rapid thermal stress.
The test rapidly alternates between hot and cold zones, typically with temperature differences of up to 300°C within seconds.
Purpose and Effect
Simulates extreme and sudden environmental changes.
Detects crack initiation, delamination, or solder joint fractures.
Essential for aerospace, defense, and high-reliability electronics.
Test Conditions
Heating rate: ≥30°C/min.
Cooling rate: ≥30°C/min.
Test temperature: -75°C to +220°C.
Cycle count: typically 10–100 cycles.
LIB Industry Thermal Shock Test Chamber features an independent high-temperature zone and low-temperature zone with rapid sample transfer for immediate temperature exposure.
High-performance thermal insulation materials and fast-response temperature control systems ensure test precision and repeatability.
Specifications of Thermal Shock Chamber
Model | TS-162 | TS-340 | TS-500 | TS-1000 |
Internal Dimensions (mm) | 300×300×250 | 450×450×360 | 650×650×500 | 850×850×700 |
Interior Volume | 22L | 72L | 211L | 505L |
Pre-Heat Zone | +220°C (Ambient → +200°C ≤ 30 min) | |||
Pre-Cool Zone | -75°C (Ambient → -70°C ≤ 30 min) | |||
Temperature Fluctuation | ≤±0.5°C | |||
Temperature Deviation | ≤±3°C | |||
Temperature Recovery Time | ≤5 min | |||
Safety Protection | Over-temperature, Over-current, High-pressure, Leakage | |||
Cooling System | Mechanical compression refrigeration | |||
Control System | Programmable LCD touch controller, Ethernet connection | |||
Interior Material | SUS304 stainless steel | |||
| ||||
The types of thermal shock tests are more varied than thermal cycle tests:
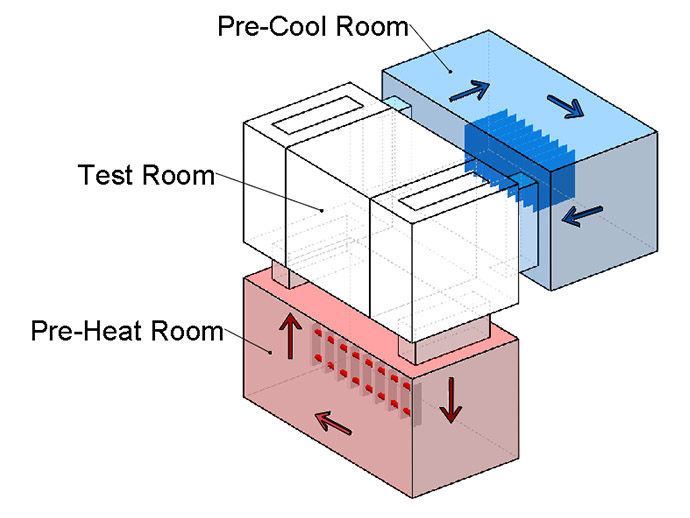
According to the structure of the thermal shock test chamber:
with high temperature, normal temperature, low temperature three zone structure and air valve switching to achieve temperature shock, the sample remains motionless in the working room, the valve of the two cold chambers and the hot chamber is opened alternately to achieve cold and heat shock test.
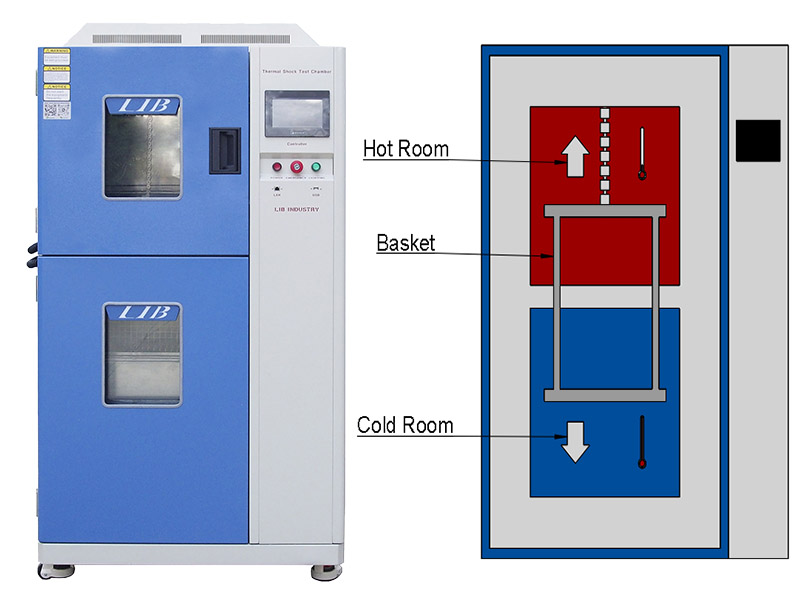
hot chamber (maximum temperature up to 220 ° C) and cold chamber (minimum temperature up to -70 ° C) and the sample in the basket rapid movement to achieve cold and thermal shock, compared with the three-chamber in terms of temperature conversion speed faster, temperature shock more harsh.
Available Test Types
Air-to-Air: rapid transfer between hot and cold air chambers.
Air-to-Liquid: heated by air, cooled in liquid for high stress load.
Liquid-to-Liquid: highest heat transfer efficiency for critical applications.
Comparison Aspect | Thermal Cycling Test | Thermal Shock Test |
Temperature Rate | Gradual (5–20°C/min) | Extremely Fast (≥30°C/min) |
Temperature Difference | Moderate | Very Large (up to 300°C) |
Cycle Duration | Long (hours–days) | Short (seconds–minutes) |
Stress Type | Progressive thermal fatigue | Instant stress concentration |
Typical Failures | Aging, deformation, fatigue | Cracks, delamination, package rupture |
Applications | Consumer electronics, automotive | Aerospace, defense, high-end components |
Recommended Products |
|
|
Summary
Thermal Cycling → Long-term reliability verification.
Thermal Shock → Resistance to sudden environmental mutation.
Using both methods helps manufacturers uncover latent defects and optimize design resilience.
With over 16 years of experience, LIB Industry delivers globally trusted environmental test chambers tailored to your application needs.
Why Choose LIB Industry
3-Year Warranty & Lifetime Technical Support
24/7 Global Service & Training
Fast Production & Delivery: 7–15 Days
1–3 Hour Custom Quotation & Proposal
Contact us today: inquiry@libtestchamber.com
Describe your testing requirements and receive a tailored quotation within hours.
Accelerate your product qualification, improve QA reliability, and ensure compliance — all with LIB Industry’s Thermal Cycling and Thermal Shock Test Chambers, the proven solution for precision, speed, and reliability worldwide.
 English
English русский
русский français
français العربية
العربية Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español 한국어
한국어 italiano
italiano tiếng việt
tiếng việt ไทย
ไทย Indonesia
Indonesia








